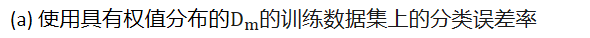Adaboost
从例子说起
有如下训练样本,我们需要构建强分类器对其进行分类。x是特征,y是标签
| 序号 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
| y | 1 | 1 | 1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | -1 |
首先明确Adaboost是通过改变训练样本的权重,学习多个分类器,并将这些分类器进行线性组合,提高分类器的性能。
因而唯一需要训练的参数就是样本的权重,训练集中有10条样本,因此,假设这10条样本的权重分别为
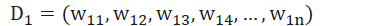
初始时,其中,N为样本的数量,即假设权重是均匀分布的。
其次,Adaboost是通过多个弱学习器组成强学习器,因此我们还要假设这些弱学习器的模型
《统计学习方法》中假设弱学习器是有x<v或x>v产生
因而无非两种形式:
G1(x) = 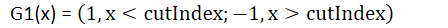
G2(x) = 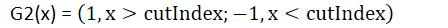
开始步骤
- 初始化权值分布
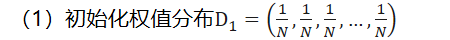
- 在权值

其中误差率为:错分的数量/样本数量
具体:选择G1- 假设cutindex=0.5,即x<0.5为1,x>0.5为-1,则预测输出为[-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1],真实输出为[1,1,1,-1,-1,-1,1,1,1,-1],因此误差率为6/10=0.6
- 假设curindex=1.5,即x<1.5为1,x>1.5为-1,则预测输出为[1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1],真实输出为[1,1,1,-1,-1,-1,1,1,1,-1],因此误差率为5/10=0.5
- …
- 最终我们可以得到G1模型,curindex=2.5时,分类误差率最低为0.3
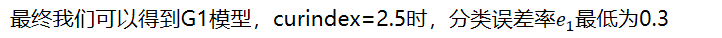
- 计算G1(2.5)的系数,推导过程后面,这里直接给计算步骤 =0.4236
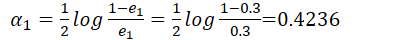
- 更新训练数据的权值分布
其中
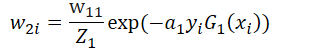
即归一化操作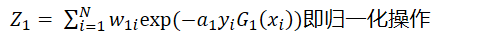
可以得到
[0.07142857142857142, 0.07142857142857142, 0.07142857142857142, 0.07142857142857142, 0.07142857142857142, 0.07142857142857142, 0.16666666666666663, 0.16666666666666663, 0.16666666666666663, 0.07142857142857142]
即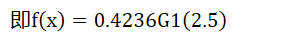
重复以上过程,我们可以得到
G1函数 cutIndex2 = 8.5
a2 = 0.6496414920651304
D3=[0.04545454545454546, 0.04545454545454546, 0.04545454545454546, 0.16666666666666669, 0.16666666666666669, 0.16666666666666669, 0.10606060606060606, 0.10606060606060606, 0.10606060606060606, 0.04545454545454546]
此时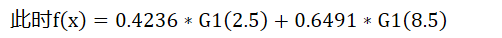
最终可以得到
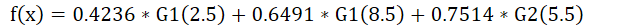
代码如下
1 | import math |
最后输出
1 | 0.4236 0.6496 0.7520 |
从原理出发
公式化以上过程
输入:训练数据集和弱学习算法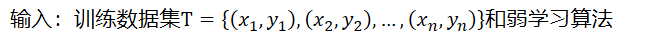
其中,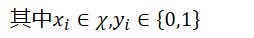
(1)初始化训练数据集的权重分布
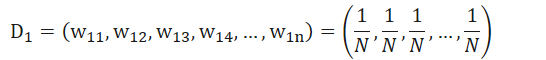
(2)对m=1,2,3,4,…,M
(a) 使用具有权值分布的